Is there still a digital divide in Australia? If so, how do we bridge that gap? If not, how do we address the apparent chasm that is leaving some “digital have-nots” behind? Is it as simple as rolling out the National Broadband Network and equipping every school child with their own tablet device? Or is it also about creating a digital mindset to ensure everyone can take advantage of the educational, social and economic opportunities that the range of digital technologies has to offer?
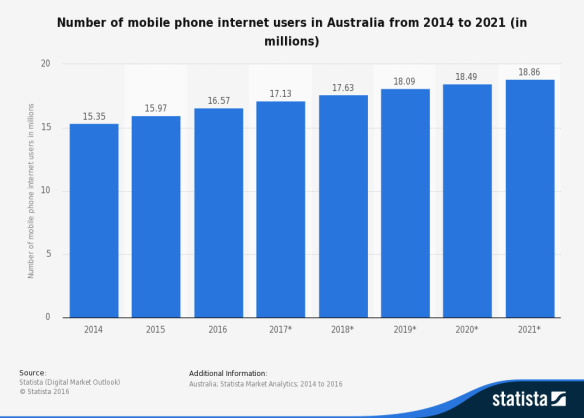
Mobile phone internet usage is projected to keep growing. Source: Statista
Based on consumer research, we would appear to be a well-connected country, with a high concentration of PC, smart phone and tablet devices, if data from Roy Morgan is any indicator. However, some recent research by Scott Ewing of Swinburne University based on ABS data has suggested that despite the narrowing of the divide, there is a deeper disconnect among those who do not have internet access.
There are multiple factors contributing to this disconnect: socio-economic, age, location and education. I would expect that within 5-10 years, age will be a far less relevant factor in who does or doesn’t have access to the internet. You could also argue that with more people accessing the internet via mobile devices, and with the increasing number of free WiFi zones across our cities (cafes, shopping centres, office buildings), public institutions (libraries, museums and galleries) and transport infrastructure (plus the reducing price of data and storage), cost may not be as much of an issue either. And once the NBN is complete, the percentage of the population without physical access to the internet should likewise be much smaller.
So that leaves education – according to the ABS-derived data, the more educated you are, the more likely you are to access the internet. Should this infer that we aren’t doing enough to teach digital skills in the classroom? Or are we teaching the wrong set of skills? Or is it a bit like learning English grammar or applied mathematics – unless you use them in your everyday life, you soon forget them, and never remember why it was important to learn them in first place?
Computer science, programming and coding courses are increasingly being taught in schools, either as part of the core syllabus or as extra-curricular activities. Many pupils have to use tablets as an integral part of their school lessons. And some schools are also running hackathons and entrepreneurial projects to help students navigate the new world of work shaped by innovation, digital disruption and the “gig” economy.
The changing nature of work is challenging schools and parents to think about how we should be preparing pupils for the future. It’s not just learning about the technology (important as it is to study data analytics, automation, robotics, AI etc.), it’s also about understanding the context and the potential for what it can do. It’s also increasingly apparent that more and more of today’s students want to do work that is meaningful, rewarding, challenging and which helps connect them to their values and “purpose”.
I like to think that as part of a well-rounded liberal education, today’s pupils will receive:
- a solid grounding in digital literacy (as important and as vital as the 3 R’s)
- an awareness of how “digital displacement” (through automation etc.) may impact their chosen career path (even in ways which we cannot yet predict – we must assume it will happen, as no profession, trade or vocation will be totally immune)
- an appetite for lifelong learning (as one of the ways to cope with the inevitable changes they will face)
- a set of life skills that instill self-awareness, curiosity, resilience, empathy, flexibility and adaptability.
Finally, if we are to truly grasp why this ability to adapt and change is important, we only need look beyond the digital debate and ask why the National Innovation and Science Agenda is failing to cut through. In large part, the NISA message failed to connect with the general electorate because many people could not identify with it, and therefore it did not resonate with them. Just as “necessity is the parent of invention”, so adversity often needs to be the catalyst for embracing change.
Notwithstanding the economic, environmental and societal challenges we face, there is considerable complacency and acceptance that “she’ll be right” – especially within the political, institutional and corporate elites that claim to lead us. As long as so few of the main actors among these bastions of power and influence decline to change their own culture, behaviours and ways of doing business, then it’s not surprising that the public feels unwilling or unable to change.
So our only real hope is to empower the next generations to shape their own future, not to be constrained by our traditional notions of “job” (in my view, an increasingly outmoded economic unit of value….) and think for themselves as to what change they want to create with all the technology, resources and opportunities at their disposal.
Next week: My Extended Gap Year