In a recent blog about geo-blocking, I commented on the frustrations of Australian consumers in trying to access digital content. That blog was written in light of a parliamentary inquiry into IT price discrimination.
 A Report by the House of Representatives Infrastructure and Communications Committee has just been published, and makes for some fascinating reading.
A Report by the House of Representatives Infrastructure and Communications Committee has just been published, and makes for some fascinating reading.
The Report reveals a number of key themes:
- There is strong evidence that Australian consumers pay between 50 and 100 per cent more for the same product than consumers in comparable markets.
- Price differentials cannot be fully explained by the so-called “Australia tax” (i.e., the relatively higher costs of doing business locally, due to wages, taxes, market regulation, shipping costs, economies of scale, etc.).
- Consumer complaints about price discrimination are not being taken seriously by the industry as a whole.
- Industry participants either deflected responsibility for price discrimination to other parts of the supply chain, or blamed inconsistent market practices as justifying the need for different regional and national price policies.
- Despite being given the opportunity by the Committee to defend their pricing practices in public, most industry participants declined to co-operate in full; this gave rise to Apple, Adobe and Microsoft each being compelled to give evidence.
- A number of submissions made by industry participants appeared to be disingenuous, self-serving, evasive and even misleading.
The Committee accepts that IT vendors are entitled to run their businesses as they see fit, and there is nothing to stop them from charging whatever prices they like. There was also general acknowledgment that copyright holders must be able to protect their IP assets.
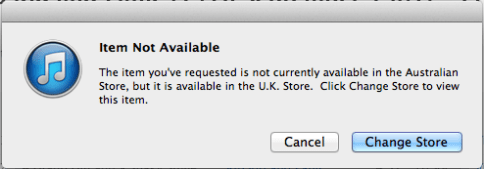
However, geo-blocking (especially of digital content) simply reinforces price disparity based on a customer’s geographical location, rather than protecting the interests of copyright holders. Further, although so-called “Technological Protection Measures” (TPM) or “Effective Technological Measures” (ETM) and “Digital Rights Management” systems (DRM) may have a legitimate role in controlling copyright (and as such they enjoy protection under the relevant Copyright Law), their net effect has been to limit competition and to lock consumers into “walled gardens” which places considerable power in the hands of IT vendors as to how, when and where consumers access content.
In short, the Committee made several recommendations designed to address price discrimination and restricted market access imposed on Australian consumers, including:
- Remove any remaining restrictions on parallel imports (in a bid to increase market competition among distributors and retailers).
- Clarify the legal circumvention of TPM/ETM/DRM barriers that are purely designed as geo-blocking tools (rather than copyright protection measures).
- Educate Australian consumers about their ability to buy cheaper goods from overseas, or to legally circumvent geo-blocking (without compromising product warranties or infringing copyright).
- As a last resort, place a ban on geo-blocking and outlaw contacts or terms of service that rely on and enforce geo-blocking.
Unfortunately, while this Report is of great significance to the Australian digital economy, and seeks to achieve a balance between the rights of copyright holders and the interests of consumers, it is likely to be overshadowed by concerns about tax avoidance in respect to multinational companies. No doubt Australian consumers will make a connection between global IT companies whose products they buy, and transnational tax minimization strategies linked to transfer pricing policies and the routing of content royalties and copyright licensing fees via low-tax jurisdictions.
