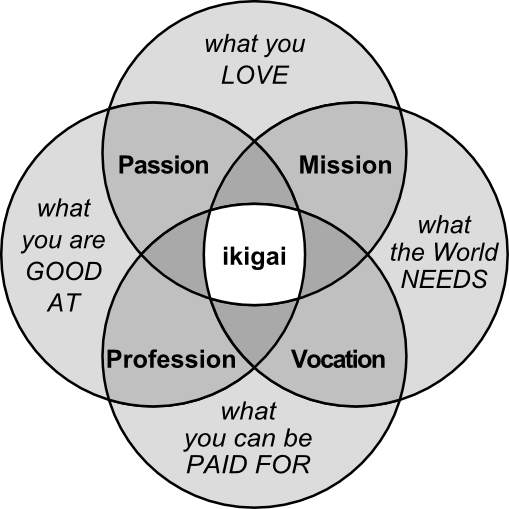
We hear a lot about “finding your purpose” these days, whether it’s to develop a personal career plan, or to validate a business idea. My colleague Carolyn Tate, founder of the Slow School of Business, spoke on “purpose” at the recent Huddle Design Fest drawing on her TEDx talk for Telstra entitled “Profit on Purpose”. During her presentation, Carolyn referenced the Japanese concept of 生き甲斐 (“ikigai” = “a reason for being”) which is sometimes represented in the following diagram:
“Finding the purpose of your life”. Graphic representation by @emmyzen (Emmy van Deurzen). Image sourced from Wikimedia Commons
What it all boils down to is connecting with your values and interests, and finding a balance between what motivates you, what rewards you, what you can contribute, and what people want from you.
For me, a the starting point is developing a personal narrative, to understand how you have arrived at this particular point in your life and/or career, in particular your influences, achievements, challenges, experiences and insights. Through this self-reflection, some common themes should emerge that can form of the basis of defining your own purpose. This should include your core values, the things that are important to you, and your own particular passion.
Where I may differ in my interpretation of “purpose” is that I believe that our purpose can change over time. I don’t see purpose as singular or even linear – it’s multi-dimensional, dynamic, situational and contextual. Our needs and our circumstances don’t stay the same. Likewise, our relationships and the the external environment are constantly changing. So our purpose will likewise be different at different points in our life. For example:
- Early in our career we may be technically qualified, but without relevant experience we may not be able to command the most senior roles or the highest pay – so our purpose may be to hone our skills and knowledge
- Later, we may find that our focus on things like marriage, children and a mortgage means we may be willing to get well-paid for work that we don’t actually enjoy – someone I was coaching recently stated that “I’m caught in a job” which was preventing him from pursuing his passion (thankfully, he has since decided to pursue a portfolio of interests, rather than stick with a single job he no longer enjoys)
- During the “third act” of our career, financial or material rewards may not be so important, but we still need to be engaged in work that we enjoy, that motivates us and which can still sustain us at more than just a basic level of food and shelter
- Throughout, I think it is essential to keep connected to our true passions (especially creative outlets), in part to provide a counterbalance to work/financial/external imperatives, in part to explore alternative ideas, find linkages between our other interests, and even to connect with new technology – for example, in my own case, my interest in electronic music has led me to recording an album using iOS devices, releasing it via social media sites Soundcloud and Bandcamp, getting it broadcast on the ABC, and beta-testing new music apps
When working with clients to help them re-connect with their business or their career purpose, I like to do an audit of where they are now, and where they could be in 3-5 years time. Through a process of exploring what might be possible, and reframing the present to re-position it for future growth and development, we can discover ways to regain balance by prioritising what’s important, reconfigure or even abandon what isn’t working, and re-establish goals and objectives.
While it is important to strike a balance between the “four pillars” of the ikigai model, my experience is that rarely will all four be in equilibrium – at times they may even be in conflict with one another, or at least in a state of flux. But it’s the resulting points of friction, when we look at them objectively, that can be the source of ideas, context, clarity and resolution. Making time for regular self-reflection enhances our pursuit of purpose, and allows us to take stock of our current situation, without undermining our core values or abandoning our particular interests.
Next week: Challenging Monocultures via Crop Rotation

